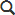Residential Electric
Vehicle Program
Need help deciding what rate is best for you?
Contact the Minnesota Power EV Group at electricvehicles@mnpower.com or by phone at 218-355-2843.
Time-of-Day Rate
Minnesota Power’s Time-of-Day rate provides the opportunity to save money by shifting your home’s electricity usage from On-Peak hours to Off-Peak or Super Off-Peak hours. Energy used during On-Peak hours will cost more, energy used during Off-Peak hours will cost less, and energy used during Super Off-Peak hours will cost the least. Your efforts to reduce electricity usage during On-Peak times allows Minnesota Power to reduce costs and pass those savings on to you. This rate applies to your entire home, not just electric vehicle (EV) charging, so there’s no need to install an additional meter. This provides an opportunity to save money on things such as dish and clothes washing.
The graphic below reflects the standard residential rate along with the Time-of-Day Rate adjustments and discounts. You can find more details on this rate here.
Weekday Time-of-Day Hours

Weekend and Holiday* Time-of-Day Hours
Residential EV Service Rate
The Residential EV Service rate offers a discounted rate for EV charging at home. This rate requires a separate metered service with its own meter socket that is wired to a dedicated electric service panel. The costs of adding this service will vary. Contact us to start an application and get advice on next steps. Customers that elect to add the Residential EV Service are eligible for a $500 EV Second Service Rebate (rebate application below).
Weekday EV Service Time-of-Day Hours

Weekend and Holiday* EV Service Time-of-Day Hours

Dual Fuel Standard Rate

Service Charge: $6.00/month
Visit our Dual Fuel Webpage for more details on this rate.
*Requires separate metered service ¹Standard rate: $0.10772 per kWh
| Rebates for EV owners | Amount | Dates |
|---|---|---|
| Rebate for adding Electric Vehicle Service | $500* |
Until 12/31/2026
Terms & Conditions apply. |
| Level 2 Smart Charger Rebate | $500* |
Until 12/31/2026
Terms & Conditions apply. |
Rebate for adding Electric Vehicle Service: Apply Here
Customers participating in Minnesota Power’s Residential EV Service Rate are eligible for a $500 rebate to help reduce the cost of installing a second service and meter.
Level 2 Smart Charger Rebate: Apply Here
Get a $500 rebate with the purchase of a qualified Level 2 Smart Charger. Customers must participate in one of Minnesota Power’s time-based or interruptible rates (Residential EV Service Rate, Time-of-Day rate, or Dual Fuel Standard Rate). Details on the rate options can be found in the Discounted Charging Options for Home section above. A list of qualified Level 2 Smart Chargers can be found using the eligible rebate equipment button below.
Click Here for eligible rebate equipment
Need more information?
Contact the Minnesota Power EV Group at electricvehicles@mnpower.com or by phone at 218-355-2843.
Plug-in electric vehicles
Also called PEVs, plug-in electric vehicles have a rechargeable battery instead of a fuel tank and an electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine. A PEV runs entirely on battery power, using an electric motor to propel itself. Drivers recharge the battery at a plugin or charging station instead of filling up at the gas pump. Example: Nissan Leaf.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
Known as PHEVs, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles have both a battery and a fuel tank and an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. The combination of a battery (which is predominantly recharged by electricity from a plug-in) and a gasoline-powered internal combustion engine extends the range of the vehicle. Example: Chevy Volt.
- A parallel hybrid uses both a combustion engine and an electric motor to deliver power to the vehicle’s wheels. The vehicle can be powered by just the electric motor, just the combustion engine, or a combination of both, depending on driving conditions. Example: Toyota Prius Plug-in, Ford Fusion Energi.
- A series hybrid is directly powered only by the electric motor. The combustion engine is used only to recharge the battery, acting as an electric generator that converts gasoline to electricity. This type of vehicle often is called an extended-range electric vehicle. Example: Chevrolet Volt.
Plug-in hybrids can be further categorized by the way they manage gasoline and electricity.
Hybrid electric vehicles
Also known as HEVs, hybrid electric vehicles are a type of hybrid vehicle that combines the internal combustion engine with a hybrid drive train. These vehicles improve the fuel efficiency of the internal combustion engine by powering some of the propulsion with electricity and running solely on battery power while the car “idles.” Hybrid electric vehicle batteries do not recharge by plugging in. Example: Toyota Prius.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has more about electric and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in its Green Vehicle Guide. You can also find more information here.
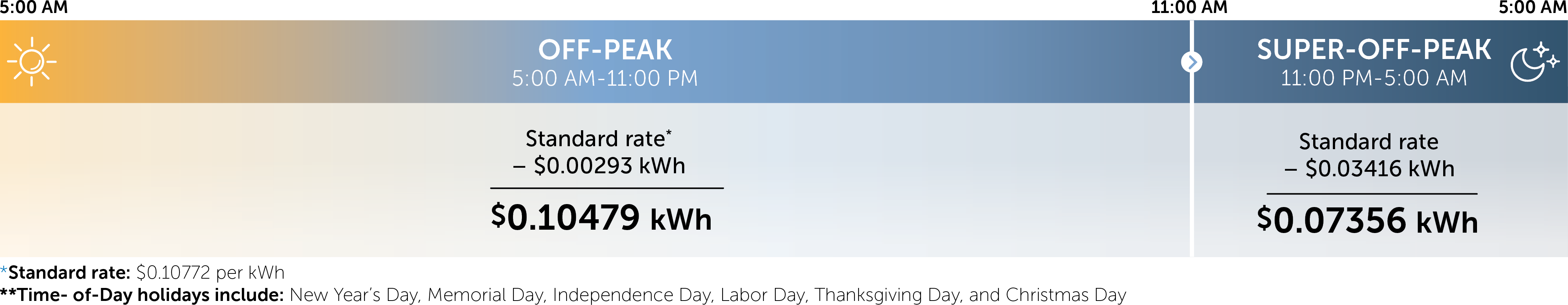
- Level 1: All plug-in vehicles come equipped with a Level 1 charging cord that can travel with the vehicle. Simply plug into a standard 120-volt electric outlet. Eight hours of charging will provide about 40 miles of range for most vehicles.
- Level 2: This requires a 240-volt connection or outlet, the same voltage a clothes dryer or water heater uses. Most EVs will get between 20 and 30 miles of range per hour of charging depending on the vehicle and charger. Level 2 chargers are commonly installed in homes and businesses and are used for the majority of EV charging.
- DC fast charger: This type of charger is typically found at public stations. They are compatible with most EVs and provide a rapid and convenient charge, typically providing a charge of up to 100 miles in less than 30 minutes.
Public Charging Stations
Expanding access to public charging infrastructure is a critical part of Minnesota Power’s efforts to support EV drivers in northern Minnesota. Minnesota Power is planning to install 16 DC fast chargers in strategic locations throughout the region* and is partnering with local businesses to provide public Level 2 charging stations.
For information about public EV chargers near you, visit Plugshare.com.
*Pending Minnesota Public Utilities Commission approval
On the homefront
Every home has the potential to be an EV fueling station, but there’s no two ways about it—charging an EV takes longer than the 10 minutes it takes to fill up at your average gas pump. Still, it’s hard to beat the convenience of plugging in at home before you go to bed and having the car ready to roll in the morning. Generally speaking, you’ll need a 120- or a 240-volt outlet and appropriate charging equipment, also known as EVSE, or electric vehicle service equipment, to charge your EV’s battery. Charging times vary by EV model and the type of charger used.
- Level 1*: All plug-in vehicles come equipped with a Level 1 charging cord that can travel with the vehicle. Simply plug into a standard 120-volt electricity outlet. Eight hours of charging will provide about 40 miles of range.
-
Level 2*:
This takes a 240-volt outlet, the same voltage an electric clothes dryer or water heater requires. You’ll get between 20 and 30 miles of range per hour of charging. Because most EV charging is done at home, EV experts recommend you install a Level 2 charger. The charging unit is about the size of a dinner plate with a long cord and costs between $300 and $3,000, depending on the brand and style of unit you purchase. Learn more at goelectricdrive.org
The complexity and cost of installing your Level 2 charger will vary depending on your personal circumstances. Some things to think about when deciding on a Level 2 charging unit:
- Hard-wired or plug-in? If you want the unit hard-wired, we recommend working with a licensed electrician. If you go the plug-in route, simply plug the charging unit into your 240-volt outlet.
- Do you have 240-volt service near your garage or where you typically park the vehicle? If you don’t, we recommend that you hire a licensed electrician to install a circuit with the appropriately sized wire and breaker for your unit. Amperage depends on the charging unit you purchase. If you have access to 240-volt service, you’ll need to identify a location for mounting the unit and decide which wiring style you’d like.
Level 2 chargers also are available at many public charging stations.
- DC fast charger*: These chargers are typically available at public stations —— you won't find them at most homes. They are compatible with most EVs and very fast, typically providing a charge of up to 100 miles in less than 30 minutes.
* Charging speeds are determined by volts and amps supplied, but other factors to consider are the top charging speed an EV will accept. Speeds are also impacted by the State of Charge (SoC) (batteries that are closer to “full” tend to curve the charge at a slower rate), as well as outside ambient temperature.
Out and about
The network of public charging stations continues to expand as more EVs hit the road. The increasing number of public options is helping to soothe any “range anxiety” EV drivers might have about running out of juice with no charging stations nearby.
Various online tools and mobile apps for locating charging stations are available. One of the most popular is PlugShare, a comprehensive and up-to-date database of EV charging stations in North America, Europe and Asia. Below is a map showing available charging stations within our service territory.
Need more information?
Contact the Minnesota Power EV Group at electricvehicles@mnpower.com or by phone at 218-355-2843.